When you’re starting a new business, having a solid business plan is super important. But knowing how to format that plan can be tricky. A good business plan format helps you organize your ideas, set clear goals, and show others why your business will succeed. In this guide, we’ll break down what a business plan format should look like, so you can create a plan that’s easy to follow and gets you the results you want. Whether you’re looking for investors or just want a clear path forward, getting your business plan format right is the first step to success.
How to Format Your Business Plan: The Cover Sheet
Every business plan should begin with a simple business plan cover page including the business name, your name and contact information. An easy to read table of contents should follow.
Example Business Plan Table of Contents
I: Executive Summary
a. Business Overview
b. Success Factors
c. Financial Highlights
II: Company Overview
a. Who is [Company Name]?
b. [Company Name]’s History
c. [Company Name]’s Products & Services
III: Industry Analysis
a. Industry Trends
IV: Customer Analysis
a. Customer Segmentation
V: Competitive Analysis
a. Direct & Indirect Competitors
b. Competitive Advantage
VI: Marketing Plan
a. The [Company Name] Brand
b. Promotions Strategy
c. Pricing Strategy
VII: Operations Plan
a. Functional Roles
b. Goals and Milestones
VIII: Management Team
a. Management Team Members
b. Hiring Plan
IX: Financial Plan
a. Revenue Model
b. Revenue and Cost Drivers
c. Key Assumptions & Forecasts
X: Appendix
The cover sheet should leave no question for readers to be able to identify the business plan when it is in a stack with dozens of others on their desk. The table of contents allows them to easily refer to sections within the plan. For example, after reading the executive summary, some investors with an eye for numbers may turn directly to the financial plan and statements. Proper business plan format allows readers to quickly get the information they want.
Example Business Plan Format
There are 10 business plan components or sections that every entrepreneur and business owner must include in their plan. These include:
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Industry analysis
- Customer analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing plan
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
- Appendix
You should recognize these if you’ve ever worked with the best business plan template.
Formatting your business plan with charts and graphs is welcomed to break up long blocks of text. However, charts and graphs shouldn’t be used for their own sake. They must make the information easier to pass on than text would.
The business plan format that investors and lenders expect includes the following 10 sections. You can download our business plan format PDF here, to help you get started. We’ve included important notes in each section specific to business plan formatting to help you as you write your plan.
1. Start with Your Executive Summary
An executive summary gives readers a crisp overview of your business at the start of your plan. This section should not be more than two pages long and should include the following:
- What is the business about?
- Where and why did the idea of the business originate?
- Who are the owners?
- Which industry is it operating in?
- What is its core function?
- Where is it located?
- How is it going to make money?
- How much money (if any) is it already making?
- What are its financial projections?
The best format for your executive summary is paragraphs. Utilizing bullets and headings is also useful formatting within an executive summary, as it aids the reader in scanning the content on the page.
2. Company Overview Section
The company overview is the perfect place to highlight the strengths of your business. This section gives the reader additional information about your products and/or services and describes your company’s past accomplishments.
Including the below in this section will provide further clarity about your business:
- What type of business you are (e.g., C-Corporation, sole proprietor)
- When your business started
- Business’ accomplishments to date
The best formatting to use in this section is paragraphs to describe your company’s strengths and products/services. You should also include a chart that outlines your company’s achievements to date.
3. Industry or Market Analysis
The industry or market analysis gives the reader a clear understanding of your industry and the audience it serves. It includes a detailed explanation of your market size and trends.
Typically, the format of this section should be paragraphs. Feel free to include charts and graphs to best convey the information to the reader.
4. The Customer Analysis States Who Your Customers Are and What They Need
In this section of your plan, explain who your target customers are and identify their specific needs. Doing this will help you better target and attract customers.
5. Competitive Analysis
The Competitive Analysis section identifies your direct and indirect competitors. It discusses who they are and their strengths and weaknesses. It then details your areas of competitive advantages.
Whether your competitors are small or large businesses, describe them. Telling investors there are no competitors (big or small) often gives the impression that a market does not exist for your company.
With regards to formatting, use paragraphs to describe each competitor. As appropriate, adding a competitor matrix to show similarities and differences between your company and the competition can be very powerful.
6. Your Marketing Plan is a Key Section
The marketing & sales section of your business plan should outline how you plan to attract new customers and retain old ones. This section should outline the ways customers can be introduced to and engage with your offerings and describe how you will convert these prospects into paying customers.
Set marketing objectives that include the following (if applicable):
- Introducing new products
- Extending the market reach
- Exploring new markets
- Boosting sales
- Cross-selling
- Creating a long-term partnership with clients
- Increasing prices without affecting sales
- Creating a content marketing strategy
Organize your Marketing Plan into the 4 P’s – Price, Product, Promotions and Place. If you have multiple products or services, include a menu with each key item and its price.
7. The Operations Plan Format
Your Operations Plan identifies your key operational processes and milestones you expect to accomplish. Using a Gantt chart is a great way to show your expected future milestones. You can also format this section with tables that document the dates of future milestones.
8. You Need to Prove Your Management Team Can Execute
“A company is only as good as the people it keeps.” – Mary Kay Ash, American Entrepreneur and Businesswoman
The Management Team section of your business plan focuses on the people who run the business.
Who are the decision-makers, who is the product expert, who is the operations head, and who is running the entire show? A glimpse into the expertise and capabilities of your team members and how their experiences will help grow your business will boost stakeholder confidence.
To improve the formatting and best convey your management team to readers, consider adding an organizational chart that shows your team members and reporting structure.
9. Format Your Financial Plan
The goal of this section is to convince the reader that your business is stable and will be financially successful. Arm this section with past and/or forecasted cash flow statements, balance sheets, profit & loss statements, expense budgeting and sales forecasts.
If you run an operational business, include 3 years of historical data to help investors gain an understanding of how feasible your funding request is and if your business is capable of generating good returns.
Also include your funding request, if applicable, in this section. You should mention how much investment is required to take your business to the next significant milestone and how the money will be spent. You should also define if you are seeking debt or equity funding. If you are seeking debt financing like an SBA loan, ensure your financial projections include the debt and show steady repayments of both the principal and return under reasonable loan terms.
If you are seeking equity financing, you don’t need to include your valuation expectations in the business plan, but you should be aligned within your ownership team on the amount of equity you are willing to exchange before you pitch investors.
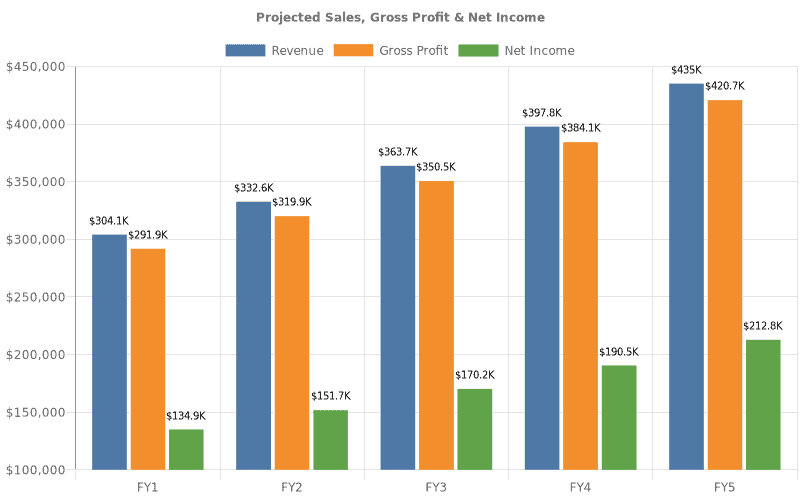
Example Financial Plan
Projected Sales, Gross Profit & Net Income
5 Year Annual Income Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Revenues | $304,128 | $332,600 | $363,738 | $397,790 | $435,031 | |
| Total Revenues | $304,128 | $332,600 | $363,738 | $397,790 | $435,031 | |
| Direct Costs | ||||||
| Direct Costs | $12,181 | $12,675 | $13,190 | $13,726 | $14,283 | |
| Total Direct Costs | $12,181 | $12,675 | $13,190 | $13,726 | $14,283 | |
| GROSS PROFIT | $291,947 | $319,925 | $350,547 | $384,064 | $420,747 | |
| GROSS PROFIT % | 96% | 96.2% | 96.4% | 96.5% | 96.7% | |
| Other Expenses | ||||||
| Salaries | $58,251 | $60,018 | $61,839 | $63,715 | $65,648 | |
| Marketing Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Rent/Utility Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Expenses | $12,135 | $12,503 | $12,883 | $13,274 | $13,676 | |
| Total Other Expenses | $70,386 | $72,522 | $74,722 | $76,989 | $79,325 | |
| EBITDA | $221,560 | $247,402 | $275,825 | $307,074 | $341,422 | |
| Depreciation | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| EBIT | $215,560 | $241,402 | $269,825 | $301,074 | $335,422 | |
| Interest Expense | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $207,560 | $233,402 | $261,825 | $293,074 | $327,422 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $207,560 | $233,402 | $261,825 | $293,074 | $327,422 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $72,646 | $81,690 | $91,638 | $102,576 | $114,597 | |
| NET INCOME | $134,914 | $151,711 | $170,186 | $190,498 | $212,824 | |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | 44.4% | 45.6% | 46.8% | 47.9% | 48.9% |
5 Year Annual Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $171,675 | $327,156 | $500,888 | $695,721 | $831,683 | |
| Other Current Assets | $26,200 | $28,653 | $31,336 | $33,149 | $36,252 | |
| Total Current Assets | $197,876 | $355,809 | $532,225 | $728,870 | $867,936 | |
| Intangible Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Intangibles | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Fixed Assets | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | |
| Accum Depreciation | $6,000 | $12,000 | $18,000 | $24,000 | $30,000 | |
| Net fixed assets | $24,000 | $18,000 | $12,000 | $6,000 | $0 | |
| Preliminary Exp | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $221,876 | $373,809 | $544,225 | $734,870 | $867,936 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Current Liabilities | $6,961 | $7,183 | $7,412 | $7,559 | $7,800 | |
| Debt outstanding | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $0 | |
| Total Liabilities | $86,961 | $87,183 | $87,412 | $87,559 | $7,800 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $134,914 | $286,626 | $456,812 | $647,311 | $860,135 | |
| Total Equity | $134,914 | $286,626 | $456,812 | $647,311 | $860,135 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $221,876 | $373,809 | $544,225 | $734,870 | $867,936 |
5 Year Annual Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $134,914 | $151,711 | $170,186 | $190,498 | $212,824 | |
| Change in Working Capital | ($19,239) | ($2,231) | ($2,453) | ($1,665) | ($2,862) | |
| Plus Depreciation | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Plus Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $121,675 | $155,480 | $173,732 | $194,832 | $215,962 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Fixed Assets | ($30,000) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Intangible Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($30,000) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from Equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from Debt financing | $80,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ($80,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $80,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ($80,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $171,675 | $155,480 | $173,732 | $194,832 | $135,962 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $171,675 | $327,156 | $500,888 | $695,721 | |
| $171,675 | $327,156 | $500,888 | $695,721 | $831,683 |
10. Appendix
This section includes supporting documentation of your business case. This could include renderings of a planned store location, market research reports referenced in the plan, key supplier or buyer contracts that substantiate your financial projections or historical marketing and sales data.
Formatting Your Business Plan
Overall, business plans should use simple and standard formatting. Twelve point font size in a standard font like Arial or Times New Roman is best, as well as the standard margin size of one inch on each side. Pages should be numbered, and the name of the company should appear on each page in the header or footer.
Use charts whenever possible as it makes it much easier for readers to consume the information in your plan.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.


 Business Plan Template Download
Business Plan Template Download How to Write a Business Plan
How to Write a Business Plan The Perfect Business Plan Outline for a Great Plan
The Perfect Business Plan Outline for a Great Plan How to Write the Business Plan Management Team Section
How to Write the Business Plan Management Team Section 100 Free Business Plan Examples
100 Free Business Plan Examples Finding a Business Plan Consultant
Finding a Business Plan Consultant How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary
How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary 10 Key Components of a Business Plan
10 Key Components of a Business Plan What is a Business Plan?
What is a Business Plan? Growthink’s Expert Business Plan Writer
Growthink’s Expert Business Plan Writer How to Create a One Page Business Plan with Template
How to Create a One Page Business Plan with Template Business Plan Software Options
Business Plan Software Options Business Plan Presentation Mistakes to Avoid
Business Plan Presentation Mistakes to Avoid How Long Should a Business Plan Be?
How Long Should a Business Plan Be? Growthink Reviews
Growthink Reviews